Exploring Moringa’s Impact On Your Thyroid
With the remarkable benefits of Moringa powder, it’s unsurprising that some individuals turn to Moringa Oleifera for thyroid support.
Approximately 20 million people in the United States experience thyroid disorders. (Source)
Let’s explore how Moringa Oleifera can contribute to enhancing thyroid hormones and, ideally, restore normal thyroid function.
How can Moringa Improve Thyroid Health to Help Thyroid Disorders?
Studies indicate that Moringa Leaves Extract aids in stabilizing TSH values affected by both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Individuals with hyperthyroidism may observe an increase in their TSH values, whereas those with hypothyroidism may witness a decrease. This establishes Moringa Leaves Extract as a promising option for thyroid management. (Source: Int. J. Pharmacol., 15 (2): 222, 2019)

Basic Thyroid Function
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in hormone production, influencing fundamental aspects of human development and hormone release into the bloodstream.
What is the difference between Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism?
Both of these conditions are related to dysfunction in the thyroid gland.
An accelerated thyroid hormone production indicates hyperthyroidism, also known as thyrotoxicosis.
On the other hand, lower-than-normal thyroid hormone production is indicative of hypothyroidism.
What is hypothyroidism
Those with hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid gland) may notice symptoms such as weight gain, constipation, sensitivity to cold, reduced sweating, fatigue, and potential changes in voice and cholesterol levels.
On the other hand, others may experience respiratory and cardiovascular issues.
Certain causes, such as iodine deficiency, manifest as the enlargement of the thyroid gland, known as goiter.
When you are experiencing low thyroid hormone levels, the pituitary and hypothalamus increase TSH production to stimulate the thyroid gland. Unfortunately, adequate thyroid function is challenging without iodine, leading to thyroid enlargement.
In some cases, thyroid disorders may be genetic.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune thyroid disease in which your body’s immune system slowly destroys the thyroid gland.
What is Hyperthyroidism
When the thyroid gland becomes overly active, producing an excess of hormones, individuals may encounter side effects.
Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland) manifests with symptoms opposite to those of hypothyroidism.
Affected individuals may experience heightened metabolism, increased activity levels, diarrhea, difficulty gaining weight, excessive sweating, and cognitive challenges like brain fog.
One of the most common causes of hyperthyroidism is Graves’ disease, an autoimmune condition marked by the presence of an antibody known as thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI).
The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid gland, shaped like a butterfly, is an endocrine gland located in the neck. Positioned below the thyroid cartilage (commonly known as the Adam’s Apple), it wraps around the trachea.
Thyroid Hormone Breakdown
The two primary thyroid hormones are T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). The naming convention is unique, with the numbers three and four indicating the iodine atoms in each hormone molecule.
Thyroid secretion is regulated by the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Notably, the anterior pituitary governs thyroid hormone secretion through TSH. This implies that thyrotropin-releasing thyroid hormone (TRH) signaled by the hypothalamus induces TSH values.
This is shown below.
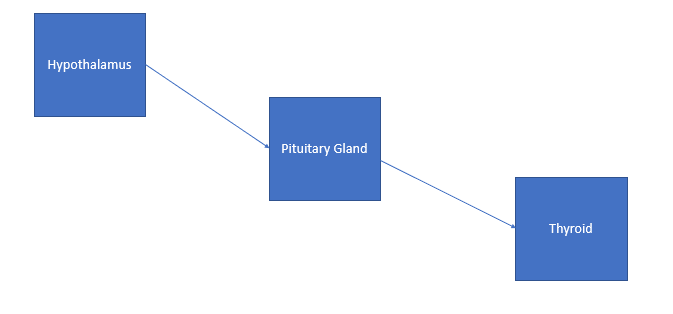 The regulation of circulating thyroid hormones involves specific feedback loops controlled by the thyroid gland. For example, when thyroid hormone levels in the blood are too high, the thyroid signals the hypothalamus to suppress these hormones. The same feedback mechanism occurs when hormone levels are too low.
The regulation of circulating thyroid hormones involves specific feedback loops controlled by the thyroid gland. For example, when thyroid hormone levels in the blood are too high, the thyroid signals the hypothalamus to suppress these hormones. The same feedback mechanism occurs when hormone levels are too low.
Graves Disease and More Powerful Thyroid Hormone
Remember earlier when we discussed thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin (TSI) from Graves’ disease?
The issue here is that when your thyroid dysfunction begins, TSI is not regulated by the same negative feedback mechanisms as before.
Moringa Oleifera and Hypothyroidism
Now that we understand what can go wrong with our thyroid hormones and thyroid gland, the next question is:
How do we fix it?
Addressing the issue can be challenging, but studies have indicated scientific improvements and remedies for hypothyroidism using Moringa Oleifera. (Source)
The use of Moringa products to manage hypothyroidism has demonstrated considerable promise, and numerous individuals are enthusiastically sharing their success stories to encourage others. (Source for Testimonials)
What is behind these remarkable effects?
Understanding Moringa and Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonoid, and flavonoids constitute a diverse group of phytonutrients (or plant chemical constituents) present in most fruits and vegetables.
Health Benefits of Quercetin
Quercetin serves as both an antioxidant and an anti-inflammatory agent, offering noteworthy effects in preventing heart disease and regulating blood sugar levels. It also contributes to alleviating aches and pains during daily activities, which is particularly beneficial for people experiencing stiffness or discomfort after waking up or exercising.
How Much Quercetin Is In Moringa?
Moringa powder is rich in quercetin, and whether you prefer to consume it as a drink or incorporate fresh Moringa leaves into your diet, each serving provides a substantial amount of quercetin.
To give you an idea, both Moringa powder and Moringa leaves contain approximately 400mg of quercetin per 100g.
How much Moringa Oleifera is usually taken for thyroid disorders?
In this study, rats were given 500mg/kg of body weight. Although this dosage is excessive for humans, a recommended starting dose would be between 500mg and 1 gram of Moringa powder. For individuals dealing with thyroid disorders or thyroid diseases, a gradual increase in Moringa powder intake to around 15 grams can be considered once the initial dosage is well-tolerated.
Can you take Moringa with levothyroxine?
It’s important to note that treating thyroid problems with levothyroxine may be affected by Moringa. Taking Moringa may potentially reduce the absorption of thyroxine. Therefore, taking Moringa and levothyroxine together might result in a decrease in their overall effectiveness.
Of course, we recommend consulting with your doctor before combining these treatments to ensure optimal results.
What herbs should I avoid with hypothyroidism?
Bugleweed (Lycopus virginicus or Lycopus europaeus) has been associated with inhibiting thyroid hormones. It is crucial to consult with a physician for more detailed information regarding thyroid hormone therapy and potential interactions with Bugleweed.
It’s important to note that these interactions are based on preliminary, weakened, incomplete, or contradictory research evidence. Seeking professional medical advice is recommended for a thorough understanding of individual health conditions and potential implications.
Can Moringa Cause Thyroid Problems?
Before Starting Moringa For My Thyroid issues, what should I do?
Before incorporating Moringa into your routine for thyroid health, it’s crucial to consult with your doctor. While research suggests numerous benefits of Moringa for the thyroid, your doctor can provide personalized guidance based on your individual health needs. It’s also important to ensure there are no potential interactions with any medications you may be currently taking. Your doctor’s expertise will help you create a safe and effective plan tailored to your specific health conditions.
Our guide, Moringa 101, can be found in the article below:
Conclusion

For years now, Moringa has been a daily consumption in my life, incorporated in various forms such as capsules, food recipes, and soothing teas. Initially, my daughter and I embarked on this journey as an experiment, but as time went on, I delved deeper into its remarkable potential and unearthed the unlimited benefits it offers for our well-being and health. I got motivated by how much it positively impacted me and decided to share my insights about Moringa’s profound impact on health and overall living through my blog posts.


